Predicate: Definition, Types & Examples
Predicate: Definition, Types & Examples
Definition of Predicate in English Grammar
Definition of Predicate in English Grammar:
In English grammar, a predicate is a fundamental component of a sentence that provides information about the subject. It typically consists of a verb and any accompanying information or modifiers. The predicate indicates what the subject is doing or what is being done to the subject.
Common elements of a predicate include:
- Verb: The action word that describes what the subject is doing or the state of being.
- Direct Object: The noun or pronoun that receives the action of the verb.
- Indirect Object: The noun or pronoun that identifies the recipient of the direct object.
- Complement: Additional words that complete the meaning of the verb, such as adjectives or adverbs.
- Modifiers: Words that provide additional information about the action or the subject.
Understanding the role of the predicate is essential for constructing clear and coherent sentences in English. It helps convey the complete thought or idea that the sentence is expressing.
Types of Predicates
Types of Predicates:
- Simple Predicate:
- Consists of the main verb in a sentence.
- It tells what the subject of the sentence is doing.
- Complete Predicate:
- Includes the main verb and all the words that give more information about it.
- It provides details about the action or state of the subject.
- Compound Predicate:
- Contains two or more verbs sharing the same subject.
- Each verb can stand alone in a sentence.
- Predicate Adjective:
- Modifies the subject of the sentence.
- It describes a characteristic or quality of the subject.
- Predicate Nominative:
- Renames or identifies the subject.
- It follows a linking verb and restates the subject.
- Predicate Adverb:
- Modifies the verb in a sentence.
- It provides information about how, where, when, or why the action is taking place.
Simple Predicate
**A simple predicate in grammar is a crucial component of a sentence that helps to convey the action or state of being of the subject. It consists of only the verb or verb phrase that tells what the subject is doing or being.
Here are some key points about simple predicates:
- Essential Element: The simple predicate is essential in a sentence as it provides crucial information about the action or state of being of the subject.
- Single Verb: It typically consists of a single main verb, but can also include a helping verb or auxiliary verb in certain cases.
- Focus on Verb: The main focus of the simple predicate is on the verb and how it relates to the subject in terms of action or being.
- Example: In the sentence “She runs every morning,” the simple predicate is “runs,” which is the main action performed by the subject “She.”
- Using Phrases: Sometimes, the simple predicate may also include verb phrases that consist of a main verb and one or more helping verbs. For example, “They have been studying for hours.”
- Distinguishing Feature: It is important to distinguish the simple predicate from the complete predicate, which includes not only the main verb but also any accompanying words that modify or complete the action.
In conclusion, mastering the concept of a simple predicate is essential for understanding the structure and meaning of sentences in grammar. It helps in clarifying the main action or state of being of the subject and contributes to effective communication in writing and speaking.
Complete Predicate
Complete Predicate in Grammar
The complete predicate is a key concept in grammar that refers to the part of a sentence that includes the verb and all its modifiers and complements. It provides more information about the action or state of being expressed by the subject of the sentence.
Components of a Complete Predicate:
- Verb: The core element of the complete predicate, it denotes the action or state of being.
- Modifiers: Words or phrases that provide additional information about the verb, such as adverbs or adverbial phrases.
- Direct Object: The noun or pronoun that receives the action of the verb.
- Indirect Object: The noun or pronoun that indicates to whom or for whom the action is done.
- Predicate Nominative: A noun or pronoun that renames or identifies the subject of the sentence after a linking verb.
- Predicate Adjective: An adjective that describes the subject of the sentence after a linking verb.
Example of a Complete Predicate:
Sentence: “Sheila is a talented singer.”
- Subject: Sheila
- Complete Predicate: is a talented singer
- Verb: is
- Predicate Nominative: singer
- Predicate Adjective: talented
Compound Predicate
A Compound Predicate in grammar consists of two or more predicates that share the same subject. This common subject is not repeated in the sentence, which allows for a more concise and structured expression of multiple actions or characteristics.
Characteristics of Compound Predicate:
- Multiple Actions: It allows the writer to express multiple actions carried out by the same subject without repetition, thus enhancing the flow and coherence of the sentence.
- Variety: It adds variety to the structure of the sentence, making it more interesting and engaging for the reader.
- Clarity: Despite containing multiple predicates, a compound predicate helps maintain clarity in the sentence as the subject remains the focus throughout.
Examples of Compound Predicate:
- The dog barked loudly and wagged its tail enthusiastically.
- She sang a melodious tune and danced gracefully on the stage.
- The students studied diligently, participated in extracurricular activities, and excelled in their exams.
In conclusion, a Compound Predicate in grammar streamlines sentence structure by enabling the inclusion of multiple actions under a single subject, fostering clarity and efficiency in communication.
Predicate: Definition, Types & Examples
Predicate Examples in Simple Sentences
Predicate Examples in Simple Sentences
In grammar, a predicate is one of the two main parts of a sentence that gives information about the subject. It includes the verb and all the words that describe the action or state of being. Here are some examples of predicates in simple sentences:
- Simple Predicate:
- She runs every morning.
- Complete Predicate:
- The cat slept peacefully on the windowsill.
- Compound Predicate:
- He likes to play basketball and he enjoys swimming.
- Predicate Nominative:
- Sarah is a doctor.
- Predicate Adjective:
- The flowers are beautiful.
- Implied Predicate:
- Are you ready? (to go)
Understanding different types of predicates can help in forming clear and concise sentences while conveying the intended message effectively.
Predicate Examples in Compound Sentences
Predicate Examples in Compound Sentences:
In compound sentences, each independent clause has its own predicate. A predicate is essential in conveying the action or state of the subject within a sentence. Here are some examples of predicates in compound sentences:
- Example 1:
- Sentence: Sarah ran the marathon, and John cheered her on.
- Predicates:
- “ran the marathon” in the first clause
- “cheered her on” in the second clause
- Example 2:
- Sentence: The team won the championship, but they celebrated modestly.
- Predicates:
- “won the championship” in the first clause
- “celebrated modestly” in the second clause
- Example 3:
- Sentence: David booked the tickets, and Emily packed the snacks.
- Predicates:
- “booked the tickets” in the first clause
- “packed the snacks” in the second clause
- Example 4:
- Sentence: The sun set beautifully, and the stars twinkled brightly.
- Predicates:
- “set beautifully” in the first clause
- “twinkled brightly” in the second clause
- Example 5:
- Sentence: The company launched a new product, yet their sales declined.
- Predicates:
- “launched a new product” in the first clause
- “sales declined” in the second clause
In compound sentences, predicates play a crucial role in expressing the actions, conditions, or relationships of the subjects within each independent clause effectively.
Predicate: Definition, Types & Examples
Predicate Examples in Complex Sentences
Predicate Examples in Complex Sentences:
In complex sentences, the predicate plays a crucial role in conveying the action or state of being performed by the subject. Here are some examples of predicates used in complex sentences:
- Simple Predicate: Expresses the main action or condition in a sentence.
- She sings beautifully.
- Complete Predicate: Includes the main verb and all its modifiers and complements.
- The students have been studying diligently for their exams.
- Compound Predicate: Contains two or more verbs sharing the same subject.
- He cooked dinner and cleaned the kitchen.
- Predicate Nominative: Renames or identifies the subject.
- She is a teacher.
- Predicate Adjective: Describes the subject of the sentence.
- The flowers smell fragrant.
- Predicate Adverb: Modifies the verb and provides more information about the action.
- He swims quickly in the pool.
- Predicate Gerund: Utilizes a verb form ending in -ing that functions as a noun.
- His favorite hobby, painting, brings him joy.
In complex sentences, the predicate plays a vital role in conveying the complete meaning and adding depth to the overall structure.
Test in a Predicate
A test in a predicate is a critical aspect of ensuring the accuracy and reliability of data analysis and decision-making processes. It involves examining the validity and performance of a particular predicate within a given context.
By conducting tests, researchers and analysts can assess the effectiveness of the predicate in producing accurate results and identifying any potential errors or inconsistencies. This helps in enhancing the overall quality of data analysis and ensuring the credibility of findings derived from the predicate.
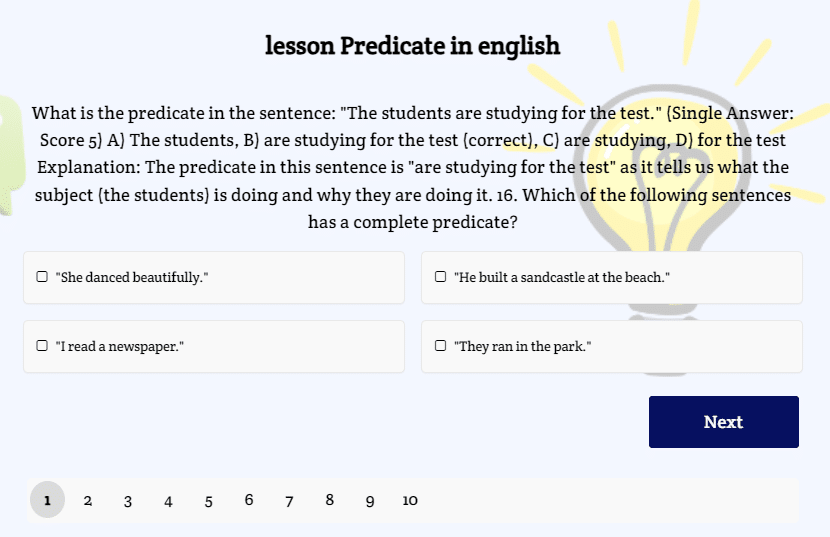
Test in today’s lesson on the second page
Table of Contents




Wwbravem01@gmail.com
I want to study English
And speak it fluetly
Learn English speaking fluetly and understanding the use of preposition l will be very great full if you accept it
nabiomgebremichael@gmail.com is my gmail
I went to have English skills as much as possible fluently .
Important subject
It is my great pleasure and happiness to understand the lecture on the predicate as a very crucial components of English grammar, and spoken ability without flaws,I really enjoyed the lecture hence I appreciate the lecturers good job.
enseignantblackm5@gmail.com
Predicate is very crucial in making sentences while speaking in English language,it is vitally important to learn all components of English language for mastery of the language, hence I will continue to learn English language with very good Text books and English Dictionary to give me much understanding.
With what I have learned so far about predicate as an important component in sentences when speaking English language I’m well satisfied and determine to continue to study more for full understanding.
I have learned much about predicate and made comments, although I shall continue to learning because I see myself as an English language student who which to master well most of the mechanic of the English language grammar.