proper noun definition & examples
proper noun definition & examples
proper noun definition
Proper nouns designate the distinctive names of individuals, locations, or objects. In English, proper nouns are always capitalized, with the first letter in uppercase. To understand more about the definition, rules, and examples of proper nouns, read the complete article.
Pronoun Definition and Examples
Merriam-Webster describes proper nouns as “a noun (like Seattle, Joyce, or Empire State Building) that identifies a specific person, place, or object, does not require a limiting modifier, and is generally capitalized in English. It is also referred to as a proper name.”
Based on the definition provided earlier, we understand that:
A proper noun is also referred to as a proper name.
A proper noun refers to a specific individual, location, or item.
Typically, articles and determiners are not placed in front of a proper noun.
In English, a proper noun is usually written with a capital letter.
Proper Noun Examples:
a. John is my friend.
b. Zurich draws in countless visitors.
c. The New York Times is a publication that comes out on a daily basis.
The bolded names or nouns are proper nouns. These denote the unique names of a person, a place, and a thing, respectively.
How to Identify a Proper Noun?
To recognize a proper noun, consider the following aspects about a proper noun:
A proper noun refers to a specific person, place, or thing. It is always written with a capital letter and generally does not take articles or determiners. For instance, “John” is a proper noun because it names a specific person. The initial letter “J” in John is always capitalized. Typically, proper nouns do not require articles or determiners, which is why we do not say “the John” or “a John.”
john is here. (incorrect)
The John is here. (incorrect)
That/my John is here. (incorrect)
Types of Proper Nouns
Proper nouns encompass, but are not limited to, the following examples:
Names of individuals, such as John, Sofia, and Maria, are particular and thus fall under the category of proper nouns.
Place names, like America, India, Japan, and others, fall into the category of proper nouns.
Titles of individuals, like President Abraham Lincoln, Alexander the Great, and Khali the Great, are also regarded as proper nouns.
Weekday Names: Days of the week like Sunday, Monday, Tuesday, etc., are considered proper nouns as well.
Month Names: The names of the 12 months, including January, February, March, and the rest, are considered proper nouns.
Brand and company names like Facebook, Google, and Pizza Hut are examples of proper nouns.
Title Names of Books, Magazines, Newspapers, and Films: Titles like Arabian Nights, Reader’s Digest, Hindustan Times, and Coming to America are considered proper nouns.
Names of Celebrations: Titles like Christmas, Eid, Holi, and so on are considered proper nouns.
Proper Noun VS Common Noun
The key distinction between a proper noun and a common noun is that a proper noun is a specific name used to identify a unique person, place, or thing, whereas a common noun is a general term used to refer to a category or type of person, place, or thing.
A proper noun is always capitalized regardless of its position in a sentence, whereas a common noun is only capitalized when it appears at the beginning of a sentence.
Rules of Proper Noun Capitalization
Rule 1: Always capitalize a proper noun, whether it appears at the beginning, middle, or end of a sentence.
Example:
John inquired Sofia about her friend Veronica.
Rule 2: Always capitalize a proper noun, even when it is functioning as a common noun.
Example:
John is the Newton of our class.
Incorrect: John is the genius of our class.
Rule 3: Do not use capital letters for the names of seasons, general subjects, or general titles when they are not at the beginning of a sentence.
Examples:
I’ll go to my village during the winter season.
I plan to go to my village during the winter season.
Correct: I study physics.
I am a Physics student.
Sure! Here’s a paraphrased version of that paragraph: “Obama, the President of the United States, is scheduled to visit Japan next week.”
Sure, here is the paraphrased paragraph: President Obama will be traveling to Japan next week.
Incorrect: Obama, the President of the US, will visit Japan next week.
Rule 4: Do not use capital letters for the words “sun” and “moon” when they are not being mentioned as astronomical objects.
Examples:
Sure! Here’s a paraphrased version: I rarely ever go to the movies.
Incorrect: I go to the movies very rarely.
Sure, here’s a paraphrased version of the paragraph: John left the room and took a seat in the sunlight.
John left the room and sat in the sunlight.
Rule 5: Words derived from a proper noun are typically capitalized.
Examples:
Certainly! Here’s a paraphrased version of the given paragraph: John is from America, while his wife hails from Japan.
John is an American and his wife is Japanese.
proper noun definition & examples
Proper Noun Definition
Proper Noun Definition
A proper noun is a specific name used to designate a unique individual, place, organization, or thing, thereby differentiating it from all others of the same category.
Unlike common nouns, which denote general items or concepts (such as “city” or “man”), proper nouns uniquely identify one particular entity (like “New York” or “Albert Einstein”). Proper nouns are always capitalized, regardless of their position in a sentence.
Key Characteristics of Proper Nouns:
Specificity
Proper nouns refer to a unique entity.
Capitalization
Always start with a capital letter.
Uniqueness
Distinct from other nouns in the same category.
Examples of Proper Nouns:
| Category | Proper Noun |
|---|---|
| Person | Albert Einstein |
| Place | New York |
| Organization | United Nations |
| Event | World War II |
| Brand | Microsoft |
Usage in Sentences:
Person: “Albert Einstein developed the theory of relativity.”
Place: “New York is known as ‘the city that never sleeps’.”
Organization: “The United Nations was founded in 1945.”
Event: “World War II had a profound impact on global history.”
Brand: “Microsoft is a leading technology company.”
Understanding and properly utilizing proper nouns is crucial for clear and specific communication in both written and spoken language.
Common Noun and Proper Noun
Certainly! Here is a paragraph and a list explaining Common Nouns and Proper Nouns in a professional tone and third person point of view.
In the English language, nouns play a critical role in sentence construction and meaning. Nouns are broadly categorized into two types: Common Nouns and Proper Nouns.
Common Nouns are general names for a group of people, places, things, or ideas. They serve as a collective identifier that is not specific to a certain individual entity.
Examples include “city,” “dog,” and “book.” On the other hand, Proper Nouns specify particular names of people, places, organizations, and sometimes things.
They are always capitalized, regardless of their position in a sentence. Proper Nouns provide specificity and uniqueness, such as “New York,” “Fido,” and “War and Peace.”
List:
Common Noun Characteristics:
General names
Not specific to one particular entity
Examples include common terms like “teacher,” “river,” and “computer”
Proper Noun Characteristics:
Specific names
Always capitalized
Examples include distinctive names like “Mr. Smith,” “Amazon River,” and “Microsoft”
| Aspect | Common Noun | Proper Noun |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | General names for a group or class | Specific names of particular entities |
| Capitalization | Not normally capitalized | Always capitalized |
| Example – Person | teacher | Mr. Smith |
| Example – Place | city | New York |
| Example – Thing | book | War and Peace |
This clear differentiation helps in enhancing the grammatical accuracy and richness of one’s language skills.
Is Mom a Proper Noun
Is “Mom” a Proper Noun?
When it comes to the English language, understanding the difference between proper nouns and common nouns is essential. Proper nouns are specific names of people, places, or things and are always capitalized, while common nouns are general names. The term “Mom” can function as both a proper noun and a common noun, depending on its usage in a sentence.
As a proper noun, “Mom” is used as a specific name or title. For example:
“I will ask Mom if I can go to the party.”
Here, “Mom” is a specific person, treated as a name and therefore capitalized.
As a common noun, “mom” is used more generally to refer to any mother:
“Every mom loves her children.”
In this context, it refers to mothers in general and is not capitalized.
Key Points:
Proper Noun Usage:When referring to a specific individual, typically replacing the person’s name.
“Sarah gave the gift to Mom.”
Common Noun Usage:When talking about mothers in general or the concept of a mother.
“Being a mom is a rewarding job.”
Table Summary:
| Context | Type of Noun | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Specific Person | Proper Noun | “Can you please help me, Mom?” |
| General Concept | Common Noun | “A mom’s work is never done.” |
Understanding these distinctions can enhance one’s grasp of grammar and proper usage within the English language. In conclusion, “Mom” can be a proper noun or a common noun based on its context within a sentence.
proper noun definition & examples
Test in a lesson proper noun
In the study of the English language, one encounters proper nouns, a fundamental concept that plays a critical role in effective communication. Unlike common nouns, which refer to general items or concepts, proper nouns are specific names of people, places, or organizations. This introduction aims to elucidate the importance and usage of proper nouns in both written and spoken English.
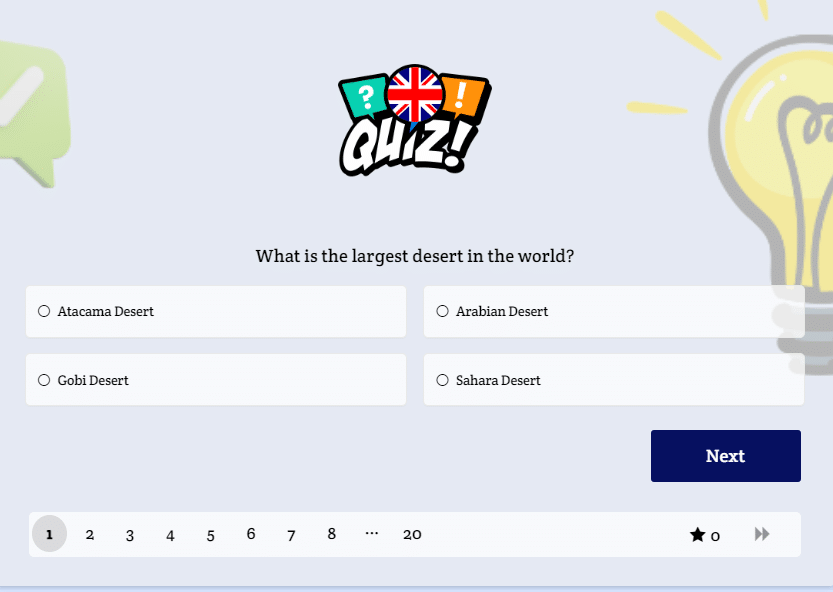
Test in today’s lesson on the second page
Table of Contents





Understanding the usage of proper nounce is crucial in spoken English language,it cannot be over emphasised,it point to the directions to go when we are speaking generally at any occasion or delivering a speach, like order components of English language grammar,one needs to learn well.